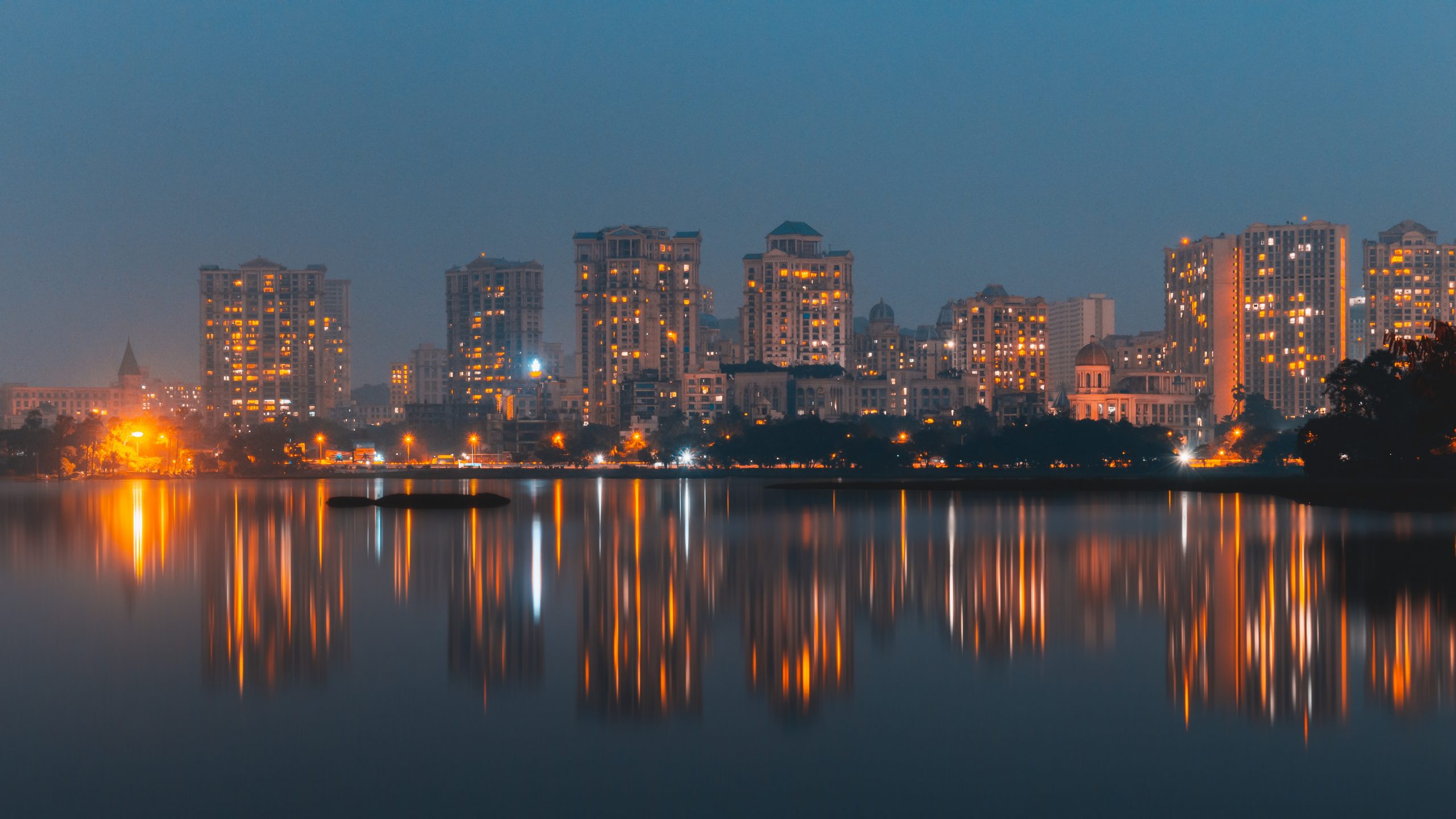
Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi established the Smart Cities Mission in the country on June 25, 2015. The objective of Smart City India attempts to enhance the quality of life for people living in India and propel economic development. Nearly 31% of the Indian population lives in cities, and they add to 63% of the GDP, according to the data gathered in Census 2011. By 2030, it is deemed that approximately 40% of India will be staying in cities and contribute 75% to the GDP.
The goal of the Indian government is to enhance quality of life in 100 cities and towns. The point of the project is to enhance a compact region within a city via retrofitting or re-development of a present built-up area or greenfield development of a vacant place. Let’s take a look at smart cities in MMR region and their development.
Smart City Mission in MMR
Under the Smart City Mission, there are four various smart cities in the Mumbai Metropolitan Region – Greater Mumbai, Navi Mumbai, Thane, and Kalyan-Dombivili. The smart city proposals of these cities concentrate on developing specific pockets of the city – Lower Parel in the case of Mumbai and Koperkhairane in the case of Navi Mumbai – and also add to the deployment of smart technologies.
Interestingly, the municipal corporations of a couple of these cities had expressed doubts about the governance structure of the suggested smart cities, and ultimately, none of the cities in the area were chosen in the first round of funding under the mission.
Apart from the Smart City Mission, the City & Industrial Development Corporation – a state government agency, is coming up with the seven southern nodes – Kalamboli, Kharghar, Kamothe, Pushpak, Ulwe, Dronagiri, Panvel, – in its Navi Mumbai (South) Smart City project.
Spread across approximately 230 acres, the corporation also has a greenfield urban development project close to the new Navi Mumbai airport called the Pushpak Nagar Smart City. A significant amount of the progress in the Navi Mumbai Airport Influence Notified Area, which encompasses 561 sq. km., is also promoted as a ‘smart city.’
The Mumbai Metropolitan Region Development Authority is believed to be the other state agency that is part of the smart city project. It is developing Bandra Kurla Complex (BKC) as a smart city by offering Wi-Fi connectivity, surveillance systems, and a smart parking facility. It is also growing 5 hubs along the suggested 126-km Virar-Alibaug Multi-Modal Corridor– Vasai-Virar, Bhiwandi, Greater Kalyan, Greater Panvel, and Pen-Alibaug– like smart cities.
As the case of Smart City MMR elucidates, numerous avatars of smart cities are being constructed in several locations. The narrative on smart cities in India is therefore not limited to cities under the government’s Smart City Mission. Instead, the term is being used for an array of modernist urban projects whether it’s developing new cities, making use of technological fixes to cities, creating hubs along industrial corridors, retrofitting specific regions within a city, or constructing private townships.
If you wish to book a property in any of the smart and developing cities of MMR, you can use IndexTap to take a look at the residential properties registered there.
Visit IndexTap for more such exciting analysis and details on real estate.